-

Derivation of Adams Method for the Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Via Computer Algebra
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
167-170
Received:
26 September 2016
Accepted:
3 March 2017
Published:
4 July 2017
Abstract: In this paper, a well-known computer algebra system (CAS) was considered for the derivation of Numerical method for the solution of initial value problems. This was achieved by the use of maple software. Numerical methods were derived through Lagrange interpolation method. Both the implicit and explicit method was derived with the help of the Computer algebra system. In particular, a review of Maple’s functional role in the derivation of numerical methods was also presented. The main challenge was that the efficient handling and simplifying of very long expressions, which was met by the power of Maple’s build-in functionality. The use of the maple procedure had significantly reduced the errors and hence improved efficiency in derivation of higher order Adams Methods.
Abstract: In this paper, a well-known computer algebra system (CAS) was considered for the derivation of Numerical method for the solution of initial value problems. This was achieved by the use of maple software. Numerical methods were derived through Lagrange interpolation method. Both the implicit and explicit method was derived with the help of the Compu...
Show More
-

Gesture Control Robotic Arm Using Flex Sensor
Waseem Afzal,
Shamas Iqbal,
Zanib Tahira,
Mehtab Ejaz Qureshi
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
171-176
Received:
7 March 2017
Accepted:
24 May 2017
Published:
12 July 2017
Abstract: The design and implementation of a gesture control robotic arm using flex sensor is proposed. The robotic arm is designed in such a way that it consists of four movable fingers, each with three linkages, an opposing thumb, a rotating wrist and an elbow. The robotic arm is made to imitate the human hand movements using a hand glove. The hand glove consists 5 flex sensor for controlling the finger movements and an Accelerometer for the wrist and elbow movements. The actuators used for the robotic arm are servo motors. The finger movements are controlled using cables that act like the tendons of human arm. The robotic arm is controlled from a distant location using a wireless module. A prototype of the robotic arm was constructed and tested for various hand movements.
Abstract: The design and implementation of a gesture control robotic arm using flex sensor is proposed. The robotic arm is designed in such a way that it consists of four movable fingers, each with three linkages, an opposing thumb, a rotating wrist and an elbow. The robotic arm is made to imitate the human hand movements using a hand glove. The hand glove c...
Show More
-

Close Form Solutions of the Fractional Generalized Reaction Duffing Model and the Density Dependent Fractional Diffusion Reaction Equation
M. Hafiz Uddin,
M. Ali Akbar,
Md. Ashrafuzzaman Khan,
Md. Abdul Haque
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
177-184
Received:
21 March 2017
Accepted:
5 April 2017
Published:
14 July 2017
Abstract: The two variable (G'⁄G, 1⁄G)-expansion method is significant for finding the exact traveling wave solution to nonlinear evolution equations (NLEEs) in mathematical physics, applied mathematics and engineering. In this article, we exert the two variable (G'⁄G, 1⁄G)-expansion method for investigating the fractional generalized reaction Duffing model and density dependent fractional diffusion reaction equation and obtain exact solutions containing parameters. When the parameters are taken particular values, traveling wave solutions are transferred into the solitary wave solutions. The two variable (G'⁄G, 1⁄G)-expansion method is the generalization of the original (G'⁄G)-expansion method established by Wang et al [21].
Abstract: The two variable (G'⁄G, 1⁄G)-expansion method is significant for finding the exact traveling wave solution to nonlinear evolution equations (NLEEs) in mathematical physics, applied mathematics and engineering. In this article, we exert the two variable (G'⁄G, 1⁄G)-expansion method for investigating the fractional generalized reaction Duffing model ...
Show More
-

Research on the Application of Numerical Method in Control Theory
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
185-188
Received:
19 July 2017
Published:
19 July 2017
Abstract: Time optimal control problems of ordinary differential equations have been of great interest for decades due to their practical applications. There are mainly two ways to compute optimal times. The first one is the Switching Time Optimization method, where the switching time is taken as extra unknowns and the optimization problems is solved by nonlinear programming technique. The second one is based on the first order necessary condition for optimal control. In this paper, we extend the numerical method given in [1] for the computation of the optimal time for the time optimal control problems. In the end some examples are provided to show the efficiency of the numerical method.
Abstract: Time optimal control problems of ordinary differential equations have been of great interest for decades due to their practical applications. There are mainly two ways to compute optimal times. The first one is the Switching Time Optimization method, where the switching time is taken as extra unknowns and the optimization problems is solved by nonl...
Show More
-

New Orbital Free Simulation Method Based on the Density Functional Theory
Victor Zavodinsky,
Olga Gorkusha
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
189-195
Received:
17 July 2017
Accepted:
25 July 2017
Published:
4 August 2017
Abstract: A practical way to simulate multi-atomic systems without using of wave functions (orbitals) is proposed. Kinetic functionals for each type of atoms are constructed and then are used for complex systems. On examples of clusters containing Al, Si, C, and O it is shown that this method can describe structures and energies of multi-atomic systems not worse than the Kohn-Sham method but faster. Besides, it is demonstrated that the orbital-free version of the density functional theory may be used for finding equilibrium configurations of multi-atomic systems with covalent bonding. The equilibrium interatomic distances, interbonding angles and binding energies for Si3 and C3 clusters are found in good accordance with known data.
Abstract: A practical way to simulate multi-atomic systems without using of wave functions (orbitals) is proposed. Kinetic functionals for each type of atoms are constructed and then are used for complex systems. On examples of clusters containing Al, Si, C, and O it is shown that this method can describe structures and energies of multi-atomic systems not w...
Show More
-

A Nontrivial Product in the Stable Homotopy of Spheres
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
196-201
Received:
7 August 2017
Published:
7 August 2017
Abstract: Let
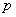
be an arbitrary odd prime number greater than eleven and
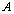
be the mod
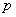
Steenrod algebra. In this paper, it has proved that the product
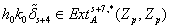
is nontrivial and converges to
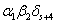
nontrivially of order
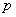
in
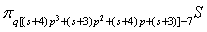
, where
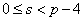
,
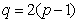
by making use of the Adams spectral sequence.
-

A Robust Preconditioned Iterative Method for the Navier-Stokes Equations with High Reynolds Numbers
Josaphat Uvah,
Jia Liu,
Lina Wu
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
202-207
Received:
13 August 2017
Published:
14 August 2017
Abstract: In this paper, we proposed a new solver for the Navier-Stokes equations coming from the channel flow with high Reynolds number. We use the preconditioned Krylov subspace iterative methods such as Generalized Minimum Residual Methods (GMRES). We consider the variation of the Hermitian and Skew-Hermitian splitting to construct the preconditioner. Convergence of the preconditioned iteration is analyzed. We can show that the proposed preconditioner has a robust behavior for the Navier-Stokes problems in variety of models. Numerical experiments show the robustness and efficiency of the preconditioned GMRES for the Navier-Stokes problems with Reynolds numbers up to ten thousands.
Abstract: In this paper, we proposed a new solver for the Navier-Stokes equations coming from the channel flow with high Reynolds number. We use the preconditioned Krylov subspace iterative methods such as Generalized Minimum Residual Methods (GMRES). We consider the variation of the Hermitian and Skew-Hermitian splitting to construct the preconditioner. Con...
Show More
-

Credibility Evaluation Algorithm Based on Deep Learning
Liu Mengling,
Li Zhendong
Issue:
Volume 6, Issue 4, August 2017
Pages:
208-214
Received:
13 August 2017
Published:
17 August 2017
Abstract: The credibility of a recommendation system is a hot focus nowadays in the field of personalized recommendation research. However, it is difficult to carry out effective credibility evaluation for the users in the presence of a false recommendation system, say nothing of eliminating suspicious users and further more improve the security and reliability of the system. This paper proposed a new method of reliability assessment based on deep learning. According to the users’ rating database, community of users with average scores is constructed and traditional credibility algorithm is used to calculate the initial credibility of the users. With the average users' reliability value as a criterion, the second assessment to the credibility based on deep learning algorithm is applied to other users, the results of which are arranged in ascending order. Then suspicious users ranking top-L will be removed and a trustfully adjacent group for the target users will be created. Experiments show that the improved algorithm can optimize the recommendation system with better security, accuracy and reliability as well.
Abstract: The credibility of a recommendation system is a hot focus nowadays in the field of personalized recommendation research. However, it is difficult to carry out effective credibility evaluation for the users in the presence of a false recommendation system, say nothing of eliminating suspicious users and further more improve the security and reliabil...
Show More







