-

Necessary and Sufficient Conditions of ε-Separability
Maria A. Ivanchuk,
Igor V. Malyk
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
28-34
Received:
13 September 2016
Accepted:
28 October 2016
Published:
21 November 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.11
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: In this paper we propose a new approach for solving the classification problem, which is based on the using ε-nets theory. It is shown that for ε-separating of two sets one can use their ε-nets in the range space w.r.t. halfspaces, which considerably reduce the complexity of the separating algorithm for large sets’ sizes. The separation space which contains the possible values of ε for ε-nets of both sets is considered. The separation space is quasi-convex in general case. To check necessary and sufficient conditions of ε-separability of two sets one can solve an optimisation problem, using the separation space as constraints. The lower bound of the separation space is convex for the exponential distribution and linear for the uniform distribution. So, we have convex and linear optimisation problems in these cases.
Abstract: In this paper we propose a new approach for solving the classification problem, which is based on the using ε-nets theory. It is shown that for ε-separating of two sets one can use their ε-nets in the range space w.r.t. halfspaces, which considerably reduce the complexity of the separating algorithm for large sets’ sizes. Th...
Show More
-

Aboodh Transform Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Third Order Korteweg -DeVries Equation
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
35-39
Received:
18 September 2016
Accepted:
21 November 2016
Published:
22 November 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.12
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: This Paper is discussing the theoretical approach of Aboodh transform [1] coupled with Homotopy Perturbation Method [3] that can be applied to higher order partial differential equations for finding exact as well as approximate solutions of the equations. Here Homotopy Perturbation Method using Aboodh transform [1], [16] has been applied to Korteweg-de vries equation which is of third order homogenous partial differential equation.
Abstract: This Paper is discussing the theoretical approach of Aboodh transform [1] coupled with Homotopy Perturbation Method [3] that can be applied to higher order partial differential equations for finding exact as well as approximate solutions of the equations. Here Homotopy Perturbation Method using Aboodh transform [1], [16] has been applied to Kortewe...
Show More
-

Uniform Approximation of the Generalized Cut Function by Erlang Cumulative Distribution Function and Application in Applied Insurance Mathematics
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
40-44
Received:
13 September 2016
Accepted:
22 October 2016
Published:
25 November 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.13
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: In this paper we study the uniform approximation of the generalized cut function by sigmoidal Erlang cumulative distribution function (Ecdf). The results are relevant for applied insurance mathematics and are intended for the actuary when preparing the strategy “Insurance responsibility”. Numerical examples are presented using CAS MATHEMATICA.
-

A Comparative Study of Homotopy Perturbation Aboodh Transform Method and Homotopy Decomposition Method for Solving Nonlinear Fractional Partial Differential Equations
Mohand M. Abdelrahim Mahgoub,
Abdelilah K. Hassan Sedeeg
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
45-51
Received:
3 October 2016
Accepted:
5 November 2016
Published:
30 November 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.14
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: In this paper, we present the solution of nonlinear fractional partial differential equations by using the Homotopy Perturbation Aboodh Transform Method (HPATM) and Homotopy Decomposition Method (HDM). The Two methods introduced an efficient tool for solving a wide class of linear and nonlinear fractional differential equations. The results shown that the (HDM) has an advantage over the (HPATM) that it takes less time and using only the inverse operator to solve the nonlinear problems and there is no need to use any other inverse transform as in the case of (HPATM).
Abstract: In this paper, we present the solution of nonlinear fractional partial differential equations by using the Homotopy Perturbation Aboodh Transform Method (HPATM) and Homotopy Decomposition Method (HDM). The Two methods introduced an efficient tool for solving a wide class of linear and nonlinear fractional differential equations. The results shown t...
Show More
-

Structural-Parametric Models and Transfer Functions of Electromagnetoelastic Actuators Nano- and Microdisplacement for Mechatronic Systems
Sergey Mikhailovich Afonin
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
52-59
Received:
12 October 2016
Accepted:
5 November 2016
Published:
30 November 2016
Abstract: Structural-parametric models, parametric structural schematic diagrams and transfer functions of electromagnetoelastic actuators are determined. A generalized parametric structural schematic diagram of the electromagnetoelastic actuator is constructed. Effects of geometric and physical parameters of actuators and external load on its dynamic characteristics are determined. For calculations the mechatronic systems with piezoactuators for nano- and microdisplacement the parametric structural schematic diagrams and the transfer functions of piezoactuators are obtained.
Abstract: Structural-parametric models, parametric structural schematic diagrams and transfer functions of electromagnetoelastic actuators are determined. A generalized parametric structural schematic diagram of the electromagnetoelastic actuator is constructed. Effects of geometric and physical parameters of actuators and external load on its dynamic charac...
Show More
-

Stochastic Modelling of the Transmission Dynamics of Measles with Vaccination Control
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
60-73
Received:
6 September 2016
Accepted:
4 November 2016
Published:
5 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.16
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: Measles is still endemic in many parts of the world including developed nations, despite the availability of the infectious disease vaccine since 1963. Elimination of measles requires maintaining the effective reproduction number by achieving and maintaining low levels of susceptibility R0 <1. In this project, we concentrate on the stochastic modelling of the transmission dynamics of measles with vaccination control. We have obtained the stochastic differential equations model from the deterministic model. Simulation of the stochastic differential equations model have been performed as well as the deterministic model. The stochastic differential equations model has described the transmission dynamics of measles with more information compared to the deterministic counterpart. Mathematical technique used in the simulation of the stochastic differential equations model is Euler-Maruyama numerical scheme and discussions of the model.
Abstract: Measles is still endemic in many parts of the world including developed nations, despite the availability of the infectious disease vaccine since 1963. Elimination of measles requires maintaining the effective reproduction number by achieving and maintaining low levels of susceptibility R0 ...
Show More
-

The Type I Generalized Half Logistic Survival Model
Phillip Oluwatobi Awodutire,
Akintayo Kehinde Olapade,
Oladapo Adedayo Kolawole
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
74-78
Received:
26 October 2016
Accepted:
10 November 2016
Published:
9 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.17
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: In this paper, a three parameter probability distribution function called type I generalized half-logistic distribution is introduced to model survival or time to event data. The survival function, hazard function and median survival time of the survival model were established. Estimation of the parameters of the model was done using the maximum likelihood method. We then applied the type I generalized half-logistic survival model to a breast cancer survival data. The derived result from type I generalized half logistic survival model was compared with the results of some common existing parametric survival models, and this revealed that the type I generalized half-logistic survival model clearly demonstrates superiority over these other models.
Abstract: In this paper, a three parameter probability distribution function called type I generalized half-logistic distribution is introduced to model survival or time to event data. The survival function, hazard function and median survival time of the survival model were established. Estimation of the parameters of the model was done using the maximum li...
Show More
-

Quaternions Algebra and Its Applications: An Overview
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
79-85
Received:
3 October 2016
Accepted:
9 December 2016
Published:
10 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.18
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: The real quaternions algebra was invented by W.R. Hamilton as an extension to the complex numbers. In this paper, we study various kinds of quaternions and investigate some of basic algebraic properties and geometric applications of them.
-

Quarkonium Masses in the N-dimensional Space Using the Analytical Exact Iteration Method
E. M. Khokha,
M. Abu-Shady,
T. A. Abdel-Karim
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
86-92
Received:
25 October 2016
Accepted:
7 November 2016
Published:
10 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.19
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: The N- dimensional radial Schrödinger equation with an extended Cornell potential is solved. The analytical exact iteration method (AEIM) is applied. The energy eigenvalues are calculated in the N –dimensional space. The charmonium meson, the bottomonium meson and the 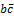 meson masses are calculated in the N-dimensional space. The special cases are obtained from the general case. The study of the effect of dimensionality number is studied. The mean value of the radius and the mean square velocity of charmonium meson, bottomonium meson, and
meson masses are calculated in the N-dimensional space. The special cases are obtained from the general case. The study of the effect of dimensionality number is studied. The mean value of the radius and the mean square velocity of charmonium meson, bottomonium meson, and 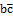 meson are calculated. The present results are improved in comparison with other recent studies and are in good agreement with the experimental data. Therefore, the present method with the present potential gives successfully description of heavy quarkonium properties.
Abstract: The N- dimensional radial Schrödinger equation with an extended Cornell potential is solved. The analytical exact iteration method (AEIM) is applied. The energy eigenvalues are calculated in the N –dimensional space. The charmonium meson, the bottomonium meson and the
meson are calculated. The present results are improved in comparison with other recent studies and are in good agreement with the experimental data. Therefore, the present method with the present potential gives successfully description of heavy quarkonium properties.
Abstract: The N- dimensional radial Schrödinger equation with an extended Cornell potential is solved. The analytical exact iteration method (AEIM) is applied. The energy eigenvalues are calculated in the N –dimensional space. The charmonium meson, the bottomonium meson and the 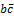 meson masses are calculated in the N-dimensional space. The special cases are ob...
Show More
meson masses are calculated in the N-dimensional space. The special cases are ob...
Show More
-

Analysis of 6061 Aluminium Alloy Sheet Metal Bending Process for Various Thickness Using Finite Element Modelling
G. Pradeep Dev,
P. Sam Livingston,
M. Shunmuganathan,
R. Surendar,
A. Siva Subramanian,
A. Simon Christopher,
K. C. Ganesh
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
93-99
Received:
6 November 2016
Accepted:
17 November 2016
Published:
10 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.20
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: This study elaborates the bending process of Al 6061 aluminium alloy using three-point bend test. The permanent deformation takes place on the sheet metal strip as a result of severe plastic strain. One of the major issues in the sheet metal bending process is that the formation of spring back during unloading. This study involves combined design of experiment and finite element analysis to understand the bending and spring back behaviour of sheet metal. The elasto-plastic behaviour is studied by parametric numerical simulations. The static mechanical behaviour at ambient temperature is investigated for various thickness and radius of punch to achieve its correlations. The systematic approach is carried by developing numerical models of three-point bending of aluminium strips.
Abstract: This study elaborates the bending process of Al 6061 aluminium alloy using three-point bend test. The permanent deformation takes place on the sheet metal strip as a result of severe plastic strain. One of the major issues in the sheet metal bending process is that the formation of spring back during unloading. This study involves combined design o...
Show More
-

Selection of Stocks on the Ghana Stock Exchange Using Principal Component Analysis
Abonongo John,
Oduro F. T.,
Ackora-Prah J.
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
100-109
Received:
19 July 2016
Accepted:
12 September 2016
Published:
10 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.21
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: A major problem in stock selection is the use of the right procedure(s) in identifying the best stock(s). The principal component analysis was employed as a data reduction technique in selecting stock(s) that characterize each sector on the Ghana Stock Exchange. The results indicated that, among the 9 stocks in the Finance sector, only 3 stocks (CAL, ETI, and GCB) were able to characterize the sector. The Distribution sector had 2 stocks (PBC and TOTAL) among the 4 stocks characterizing the sector. The Food and Beverage sector had only FML characterizing the sector out of the 3 stocks. Also, the information Technology had CLYD characterizing the sector out of the 2 stocks. The Insurance sector had EGL characterizing the sector out of the 2 stocks. The Manufacturing sector had only 2 stocks (PZC and UNIL) characterizing the sector out of the 10 stocks and for the Mining sector, 2 stocks (TLW and AGA) among the 4 stocks were the best. In effect, the 34 stocks considered from the Ghana Stock Exchange were reduced to 12 stocks (CAL, ETI, GCB, PBC, TOTAL, FML, CLYD, EGL, PZC, UNIL, TLW and AGA). The results also indicated that the selected stocks were able to explain much of the variance in their respective sectors compared to the rest of the stocks in that same sector and thus could be considered for further analysis and probably investment.
Abstract: A major problem in stock selection is the use of the right procedure(s) in identifying the best stock(s). The principal component analysis was employed as a data reduction technique in selecting stock(s) that characterize each sector on the Ghana Stock Exchange. The results indicated that, among the 9 stocks in the Finance sector, only 3 stocks (CA...
Show More
-

Russell’s Paradox, Our Solution, and the Other Solutions
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
110-114
Received:
16 October 2016
Accepted:
18 November 2016
Published:
17 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.22
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: The aim of this paper is proving that our solution is better than the solution presented by the own Russell and what is today the most accepted solution to the Russell’s Paradox, which is the solution of Zermelo and Frankael. We presented our solution a few years ago, and that is a solution that we believe should be considered to be the actual solution. We decided to do what Dr. Hyde asked us to do in 2000 in terms of The Sorites Paradox and our solution to it, which is studying all objections to all solutions that have been previously presented and then saying why our solution does not suffer from those problems. We then analyze the solution presented by the own Russell back then on top of the most accepted solution, that of Zermelo and Frankael. We do all from the most unbiased perspective as possible. We seem to be able to prove, with solid argumentation, that our solution to the Russell’s Paradox is the best solution so far. The methods we use are: analytical and synthetic studies, application of the results of the synthetic studies, and tests of soundness in reasoning based on the foundations of Logic. Each time something is found to be unsound we direct ourselves to our own solution and assess it in the same way to see if the study of ours also leads to unsoundness. Our results are that our solution is sounder than the solutions presented by Russell, Zermelo, and Frankael. The conclusion is that it is very likely to be the case that we have a final solution.
Abstract: The aim of this paper is proving that our solution is better than the solution presented by the own Russell and what is today the most accepted solution to the Russell’s Paradox, which is the solution of Zermelo and Frankael. We presented our solution a few years ago, and that is a solution that we believe should be considered to be the actual solu...
Show More
-

Multichannel MMSE Wiener Filter Using Complex Real and Imaginary Spectral Coefficients for Distributed Microphone Speech Enhancement
Marek B. Trawicki,
Michael T. Johnson
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
115-120
Received:
26 October 2016
Accepted:
26 November 2016
Published:
20 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.23
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: In this paper, the authors propose a frequency domain multichannel Wiener filter for distributed microphone speech enhancement using acoustic arrays. The current state-of-the-art single channel estimators achieve noticeable performance gains using the to-noise ratio (SNR) and segmental signal-to-noise ratio (SSNR) objective measures, which measure noise reduction, but only achieve marginal performance gains using the Log-Likelihood Ratio (LLR) and Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ) objective metrics, which correlate better than SNR and SSNR with speech distortion and overall speech quality. By extending the traditional single channel Wiener filter to multiple distributed channels through minimum mean-square error (MMSE) estimation of the complex real and imaginary components, the approach presented here demonstrates increases in the SSNR, LLR, and PESQ objective measures. Experimental results show that the new multichannel Wiener filter using distributed microphones produces gains of 5.0 dB (SSNR improvement), 0.7 (LLR output), and 0.8 (PESQ output) averaged across the 0 dB, 5 dB, and 10 dB input SNRs over the baseline single channel Wiener filter.
Abstract: In this paper, the authors propose a frequency domain multichannel Wiener filter for distributed microphone speech enhancement using acoustic arrays. The current state-of-the-art single channel estimators achieve noticeable performance gains using the to-noise ratio (SNR) and segmental signal-to-noise ratio (SSNR) objective measures, which measure ...
Show More
-

Restricted and Unrestricted Methods of Bootstrap Data Generating Processes
Acha Chigozie K.,
Nwabueze Joy C.
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
121-126
Received:
30 October 2016
Accepted:
17 November 2016
Published:
21 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.24
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: This study compares the restricted and unrestricted methods of bootstrap data generating processes (DGPs) on statistical inference. It used hypothetical datasets simulated from normal distribution with different ability levels. Data were analyzed using different bootstrap DGPs. In practice, it is advisable to use the restricted parametric bootstrap DGP models and thereafter, check the kernel density of the empirical distributions that are close to normal (at least not too skewed). In fact, 21600 scenarios were replicated 200 times using bootstrap DGPs and kernel density methods. This analysis was carried out using R-statistical package. The results show that in a situation where the distribution of a test is skewed, all the scores need to be taken into account, no matter how small the sample size and the bootstrap level are. Across all the conditions considered, models HR5UR and HPN5UR yielded much larger bias and standard error while the smallest bias values were associated with models HR5R (0.0619) and HPN5R (0.0624). The result confirms the fact that bootstrap DGPs are very vital in statistical inference.
Abstract: This study compares the restricted and unrestricted methods of bootstrap data generating processes (DGPs) on statistical inference. It used hypothetical datasets simulated from normal distribution with different ability levels. Data were analyzed using different bootstrap DGPs. In practice, it is advisable to use the restricted parametric bootstrap...
Show More
-

ABC of the Sukuma Calendar
Edward Anthony Makwaia,
Charles Edward Ng’Hwaya Masule
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
127-135
Received:
8 September 2016
Accepted:
21 November 2016
Published:
27 December 2016
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.25
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: The aim of this study had been to document and to astronomically mimic in an algorithm the undocumented ancient lunar calendar of the Sukuma and that of the Nyamwezi sibling tribe of Tanzania which is at the verge of perishing due to the perishing of living memory about that calendar. It had been found that the Sukuma calendar marks its end of the sidereal year at the Sukumaland “Jidiku” position of Earth in its trajectory around the Sun which is the December Solstice astronomically fitting on the Gregorian 23rd December. The stereotype is that the ancient Sukuma of Kishapu tallied up the elapsing days since the first appearance of the "ndimila" on the horizon day-to-day using 64 pebbles to get to the “Jidiku” and later developed that method of tallying days into the fully fledged “isolo” game of counting pebbles. Subsequent to the determination of the “Jidiku” position, the algorithm to compute the Sukuma lunar New Year was developed basing on the technique of computing the Jewish calendar in essence whereby the number of lunar-tagged days elapsed to the beginning of a 19-year lunar cycle since 01st January year 0000 get compared with the number of solar days elapsed to the beginning of a 19-year Gregorian cycle since 01st January year 0000 to get the difference in number of days short to the next new moon which mark the Sukuma lunar New Year lying between 23rd December and 22nd January. By adding the number of days short to the next new moon at the beginning of a 19-year Gregorian cycles to a series-tagged increment of days - which is a product of 19 and a within-cycle-relative year of the running year (lying between 0 and 18) - the within-cycle lunar New Year gets computed. The lengths of the consecutive lunar months between two consecutive Sukuma lunar New Years were found to fit in a model of repeating 30-to-29 days. It was further found that the Nyamwezi lunar New Year falls one lunar month before the Sukuma lunar New Year and that a Nyamwezi lunar New Year within a 19-year Gregorian cycle is gotten by adding a series-tagged decrement of days - which is a product of 11 and a within-cycle-relative year of the running year - to the begin-of-cycle number of days short to the next new moon.
Abstract: The aim of this study had been to document and to astronomically mimic in an algorithm the undocumented ancient lunar calendar of the Sukuma and that of the Nyamwezi sibling tribe of Tanzania which is at the verge of perishing due to the perishing of living memory about that calendar. It had been found that the Sukuma calendar marks its end of the ...
Show More
-

The Psychosocial Analysis of the Problem of AIDS in Azerbaijan
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
136-139
Received:
11 September 2016
Accepted:
24 November 2016
Published:
9 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.26
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: Given article is devoted one of the most serious and actual problems of modern life - a problem of AIDS which has gained the big distribution, as among youth, and other age categories of citizens. The present research was spent by means of following methods: a method of the included and latent supervision over behaviour of examinees, a method of natural experiment, a method of conversation and interview, a questioning method. The purpose of carrying out of the given research consists in revealing and detection of the fact of presence of a HIV-infected and AIDS carriers, definition of real quantity of people - carriers of these infections according to the official and informal statistics. The problem consists that in the Azerbaijan society such phenomena as prostitution, the narcotism, a HIV an infection meaningly disappear from the people subject to these defects and diseases, and accordingly, the fact of their detection occurs much later. This circumstance essentially complicates the decision of the given problems and search of real ways of the help to these people. By means of the above-stated methods it is revealed not only presence AIDS and a HIV-infected of people, both among men, and among women (a parity 4:1), but also it is revealed geography of the places of residence of these people, the various reasons and the factors generating a problem of a HIV with all that it implies are studied. As the main reasons are established: prostitution, unemployment, negative economic and social situation, propensity to bad habits, especially narcotisms and others. Result of research were conclusions about necessity of continuous psychological and medical education, increase of level of literacy, outlook, social employment, people demand that is pledge of mental health of each person and a society as a whole.
Abstract: Given article is devoted one of the most serious and actual problems of modern life - a problem of AIDS which has gained the big distribution, as among youth, and other age categories of citizens. The present research was spent by means of following methods: a method of the included and latent supervision over behaviour of examinees, a method of na...
Show More
-

Multiple Linear Regression Photovoltaic Cell Temperature Model for PVSyst Simulation Software
Victor Etop Sunday,
Ozuomba Simeon,
Umoren Mfonobong Anthony
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
140-143
Received:
25 October 2016
Accepted:
12 December 2016
Published:
9 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.27
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: In this paper, two multiple linear regression models for the determination of photovoltaic (PV) cell temperature and for selection of appropriate thermal loss factor values in PVSyst is presented. One of the linear models can determine the cell temperature with solar irradiation and ambient temperature alone while the second model requires the solar irradiation, ambient temperature and wind speed in order to determine cell temperature. The cell temperature determined from any of the two models can then be used to select the appropriate thermal loss factor for PVSysts simulation. Sample meteorological data extracted from PVSyst software meteo-file for Dakar, the capital of Senegal, in West Africa is used for the study. In agreement, the two models gave the same thermal loss factor U=30.255. Essential, the approach presented in this paper can be used to effectively determine cell temperature, with and without wind speed.
Abstract: In this paper, two multiple linear regression models for the determination of photovoltaic (PV) cell temperature and for selection of appropriate thermal loss factor values in PVSyst is presented. One of the linear models can determine the cell temperature with solar irradiation and ambient temperature alone while the second model requires the sola...
Show More
-

Duration-Based Call Management Scheme
Ezenugu Isaac A.,
Eke James,
Onoh G. N.
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
144-149
Received:
25 October 2016
Accepted:
27 December 2016
Published:
20 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.28
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: Considering some of the major challenges suffered by majority of the wireless communication network users and also the challenges being faced by the network providers in order to provide satisfactory quality of services that will meet the demand of their subscribers, there is a need for an implementation of a better call management scheme. This proposed scheme classified calls into two groups; short-calls and long-calls. Statistically, it has been found that over 65% of GSM users make calls that are less than or equal to 180s. Hence, this proposed scheme will give priority to short calls, and also adopt a relative probability factor (β) which will be used to allocate some percentage of the channels that were initially allocated to long calls whenever the long calls are minimal within the last interval being considered. This scheme tends to provide better utilisation of communication channels at all-time especially at peak periods. This paper considers the number of available channels, signal strength, short-call duration, long-call duration, call arrival rate and call service rate within the Base Transceiver Station (BTS).
Abstract: Considering some of the major challenges suffered by majority of the wireless communication network users and also the challenges being faced by the network providers in order to provide satisfactory quality of services that will meet the demand of their subscribers, there is a need for an implementation of a better call management scheme. This pro...
Show More
-

Exponential Entropy Approach for Image Edge Detection
Hassan Badry Mohamed El-Owny
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
150-155
Received:
31 October 2016
Accepted:
3 December 2016
Published:
20 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.29
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: Edge detection is an important pre-processing step in image analysis. Best results of image analysis extremely depend on edge detection. Up to now many edge detection methods have been developed such as Prewitt, Sobel, LoG, Canny, etc. But, they are sensitive to noise. In this paper we propose a novel edge detection algorithm for images corrupted with noise based on Exponential Entropy. The performance of our method is compared against other methods by using various images. It is observed that the proposed algorithm displayed superior noise resilience and decrease the computation time compared with standard approaches. The results indicate the accuracy of the proposed edge-detection method over conventional edge-detection methods.
Abstract: Edge detection is an important pre-processing step in image analysis. Best results of image analysis extremely depend on edge detection. Up to now many edge detection methods have been developed such as Prewitt, Sobel, LoG, Canny, etc. But, they are sensitive to noise. In this paper we propose a novel edge detection algorithm for images corrupted w...
Show More
-

Modelling Typhoid Fever with Education, Vaccination and Treatment
Stephen Edward,
Nkuba Nyerere
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
156-164
Received:
9 December 2016
Accepted:
27 December 2016
Published:
21 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.30
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: Typhoid is among the most endemic diseases, and thus, of major public health concerns in tropical developing countries. In this study, we develop a deterministic compartmental mathematical model for assessing the effects of education campaigns, vaccination and treatment on controlling the transmission dynamics of typhoid fever in the community. We have shown that the disease free equilibrium state of the model is locally asymptotically stable if the basic reproduction number is less than unity. Careful analysis of the effective reproduction number has shown that, each of the intervention; education campaigns, vaccination or treatment has an effect in decreasing the transmission of typhoid fever in the community. Sensitivity analysis shows that, the most sensitive parameters are recovery rate for symptomatic infectious individuals, recruitment rate, vaccination rate, education campaign and transmission rate for carrier individuals. Both numerical and analytical results suggest that multiple control strategies are more effective than a single control strategy.
Abstract: Typhoid is among the most endemic diseases, and thus, of major public health concerns in tropical developing countries. In this study, we develop a deterministic compartmental mathematical model for assessing the effects of education campaigns, vaccination and treatment on controlling the transmission dynamics of typhoid fever in the community. We ...
Show More
-

Using Lagrange Interpolation for Solving Nonlinear Algebraic Equations
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
165-169
Received:
14 November 2016
Accepted:
12 December 2016
Published:
22 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.31
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: Finding the roots of nonlinear algebraic equations is an important problem in science and engineering, later many methods developed for solving nonlinear equations. These methods are given [1-28], in this paper, a new Algorithm for solving nonlinear algebraic equations is obtained by using Lagrange Interpolation method by fitting a polynomial form of degree two. This paper compare the present method with the Famous methods of Regula Falsi (RF), Besection (BS), Modified Regula Falsi (MRF), Nonlinear Regression Method (NR) given by Jutaporn N, Bumrungsak P and Apichat N, 2016 [1] and Least Square Method (LS) given by N. IDE, 2016 [2]. We verified on a number of examples and numerical results obtained show that the present method is faster than the other methods.
Abstract: Finding the roots of nonlinear algebraic equations is an important problem in science and engineering, later many methods developed for solving nonlinear equations. These methods are given [1-28], in this paper, a new Algorithm for solving nonlinear algebraic equations is obtained by using Lagrange Interpolation method by fitting a polynomial form ...
Show More
-

Modeling and Simulation of Non-Linear and Hysteresis Behavior of Magneto-Rheological Dampers in the Example of Quarter-Car Model
Issue:
Volume 2, Issue 2, December 2016
Pages:
170-189
Received:
13 November 2016
Accepted:
2 December 2016
Published:
23 January 2017
DOI:
10.11648/j.ijtam.20160202.32
Downloads:
Views:
Abstract: This paper presents reviews of mathematical formulations and numerical simulation models of non-linear and dynamic hysteresis behaviors of magneto-rheological liquid dampers, viz. Bingham, Dahl, LuGre and Bouc-Wen models, developed in MATLAB®/Simulink® in the example of quarter-car model with the Golden Car parameters. It demonstrates numerical simulations of the magneto-rheological liquid damper models with different sets of parameters and discusses simulation results and performances of these four models for different road profile excitation signals, such as Heaviside step function, sine wave, random noise and white Gaussian noise.
Abstract: This paper presents reviews of mathematical formulations and numerical simulation models of non-linear and dynamic hysteresis behaviors of magneto-rheological liquid dampers, viz. Bingham, Dahl, LuGre and Bouc-Wen models, developed in MATLAB®/Simulink® in the example of quarter-car model with the Golden Car parameters. It demonstrates numerical sim...
Show More





















