-

A Copula Based Test for a Two Component Bivariate Mixture Distribution
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
61-66
Received:
28 August 2017
Accepted:
13 September 2017
Published:
1 November 2017
Abstract: The paper presents a Copula based approach to test for a two component bivariate mixture distribution. The regular joint density is modeled by using the Copula and then the Locally Most Powerful test (LMP) test is derived by using this Copula based regular density. This is a fairly simple test compared to the dip / depth test developed by Hartigan. Our simulation results show that this Copula based (LMP) test is very powerful in detecting a mixture.
Abstract: The paper presents a Copula based approach to test for a two component bivariate mixture distribution. The regular joint density is modeled by using the Copula and then the Locally Most Powerful test (LMP) test is derived by using this Copula based regular density. This is a fairly simple test compared to the dip / depth test developed by Hartigan....
Show More
-

Modeling Time-to- Recovery of Adult Diabetic Patients Using Cox-Proportional Hazards Model
Abiyot Negash Terefe,
Assaye Belay Gelaw
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
67-71
Received:
21 August 2017
Accepted:
7 September 2017
Published:
10 November 2017
Abstract: Diabetes is a group of diseases marked by high or low level of glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action or both. The objective of this study is to model time-to-first recovery of adult diabetic patients using Cox Proportional Hazards model. A retrospective data was obtained from Jimma University Specialized Hospital diabetic patient clinic whose age 18 years and under treatments in between September 2010 and August 2013 are included in the study. Time of fasting blood sugar level to reach the first normal range, 70-130 mg/dl of blood were the response variable. Cox Proportional Hazard model were used. Types of diabetic, bodyweight at baseline, fasting blood sugar at baseline, sex and age of patients are significantly associated with time to first recovery of diabetic patients. These variables are important factors that should be considered during the selection phase a treatment (combination of treatments) for diabetes.
Abstract: Diabetes is a group of diseases marked by high or low level of glucose resulting from defects in insulin production, insulin action or both. The objective of this study is to model time-to-first recovery of adult diabetic patients using Cox Proportional Hazards model. A retrospective data was obtained from Jimma University Specialized Hospital diab...
Show More
-

Imputation Methods for Longitudinal Data: A Comparative Study
Ahmed Mahmoud Gad,
Rania Hassan Mohamed Abdelkhalek
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
72-80
Received:
5 March 2017
Accepted:
28 March 2017
Published:
10 November 2017
Abstract: Longitudinal studies play an important role in scientific researches. The defining characteristic of the longitudinal studies is that observations are collected from each subject repeatedly over time, or under different conditions. Missing values are common in longitudinal studies. The presence of missing values is always a fundamental challenge since it produces potential bias, even in well controlled conditions. Three different missing data mechanisms are defined; missing completely at random (MCAR), missing at random (MAR) and missing not at random (MNAR). Several imputation methods have been developed in literature to handle missing values in longitudinal data. The most commonly used imputation methods include complete case analysis (CCA), mean imputation (Mean), last observation carried forward (LOCF), hot deck (HOT), regression imputation (Regress), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), The expectation maximization (EM) algorithm, and multiple imputation (MI). In this article, a comparative study is conducted to investigate the efficiency of these eight imputation methods under different missing data mechanisms. The comparison is conducted through simulation study. It is concluded that the MI method is the most effective method as it has the least standard errors. The EM algorithm has the largest relative bias. The different methods are also compared via real data application.
Abstract: Longitudinal studies play an important role in scientific researches. The defining characteristic of the longitudinal studies is that observations are collected from each subject repeatedly over time, or under different conditions. Missing values are common in longitudinal studies. The presence of missing values is always a fundamental challenge si...
Show More
-

Limit Theorems of Integrals with Respect to Vector Random Measures in Complete Paranormed Spaces
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
81-86
Received:
7 September 2017
Accepted:
26 September 2017
Published:
15 November 2017
Abstract: This paper studies random integral of the form
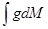
, where
f is a function taking value in a paranormed vector space
X, and
M is an independent scattered vector random measure. Random integrals of this type are a natural generalization of random series with paranormed space valued coefficients. Some limit theorems of integrals with respect to vector random measures are proved.
-

Challenges and Implications of Missing Data on the Validity of Inferences and Options for Choosing the Right Strategy in Handling Them
Nicholas Pindar Dibal,
Ray Okafor,
Hamadu Dallah
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
87-94
Received:
29 September 2017
Accepted:
17 October 2017
Published:
20 November 2017
Abstract: Missing data in surveys and experimental research is a common occurrence which has serious implications on the validity of inferences. Advances in statistical procedures provides better and efficient methods of handling missing data yet many researches still handle incomplete data in ways that affects the results negatively. We review in detail the mechanisms that generates missingness, and the appropriate methods to account for the missing values to enable the researcher have adequate knowledge to make informed decision on the choice of method to account for missingness.
Abstract: Missing data in surveys and experimental research is a common occurrence which has serious implications on the validity of inferences. Advances in statistical procedures provides better and efficient methods of handling missing data yet many researches still handle incomplete data in ways that affects the results negatively. We review in detail the...
Show More
-

Childhood Mortality Adjusting for Cluster Effect Study in Ghana Demographic Health Survey
Kankam Stephen,
Nana Kena Frimpong,
Kofi Adagbodzo Samuel
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
95-102
Received:
7 March 2017
Accepted:
5 April 2017
Published:
28 November 2017
Abstract: In Ghana Demographic Health Survey (GDHS), information is collected on the demographic characteristics and health status which is representative sample of the entire population. The backbone for the survey is enumeration areas (EA), clusters which was done using two-stage probabilistic approach. This paper illustrates analysis of childhood mortality by adjusting for cluster effect using Generalized Estimation Equations (GEE). Ghana Demographic Survey Data -2008 (GDHS-2008) was used for the analysis. GEE model with three working correlation matrices independence, unstructured and exchangeable were adjusted for the data set. Logistic regression models and statistical tools were used to find association and select significant variables on childhood mortality. Age of mother, Total birth in last five years and region of residence were significance determinants of incidence of childhood mortality. We recommend that there should be clear policy and programs for educating, campaigning and increasing and improving health facilities. Suggestions for further study of childhood mortality were also in this paper.
Abstract: In Ghana Demographic Health Survey (GDHS), information is collected on the demographic characteristics and health status which is representative sample of the entire population. The backbone for the survey is enumeration areas (EA), clusters which was done using two-stage probabilistic approach. This paper illustrates analysis of childhood mortalit...
Show More
-

Predicting Breast Cancer Incidence Rates Among White and Black Women in the United States: An Application of FTS Model
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
103-112
Received:
10 March 2017
Accepted:
29 March 2017
Published:
28 November 2017
Abstract: Development of statistical model for cancer incidence trend predictions can provide a sound and accurate foundation for planning a comprehensive national strategy for optimal partitioning of research resources. Several studies in the past showed that that there are racial/ethnic disparities exist between breast cancer incidence rates among black and white women in the United States. Some of the studies also showed that the disparity in breast cancer incidence rates among white and black US women is widening, with relatively higher incidence rates among black women. In this paper, we apply functional time series (FTS) models on the age-specific breast cancer incidence rates for these two major groups of women in US, and forecast their age-incidence curves. The data are obtained from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) program of the United States. We use annual unadjusted breast cancer incidence rates from 1973 to 2013 in 5-year agegroups (15-19, 20-24, 25-29, 30-34, 35-39, 40-44, 45–49, 50–54, 55–59, 60–64, 65–69, 70–74, 75–79, 80–84 and 85+). Age-specific cancer incidence curves are obtained using nonparametric smoothing methods. The curves are then decomposed using functional data paradigm and we fit functional time series (FTS) models for each population of women separately. The smoothed incidence curves are then forecasted and prediction intervals are calculated. Fifteen-year forecasts indicate an overall increase in future breast cancer incidence rates for both groups of women. This increase appears to be faster among black women and relatively slower among the whites. The projections suggest a need for equal delivery of quality care to eliminate breast cancer disparities among the two major groups of women in US.
Abstract: Development of statistical model for cancer incidence trend predictions can provide a sound and accurate foundation for planning a comprehensive national strategy for optimal partitioning of research resources. Several studies in the past showed that that there are racial/ethnic disparities exist between breast cancer incidence rates among black an...
Show More
-

SDG-1 and 5 Complemented by BNF at Bangladesh: An Investigation
Muhammad Mahboob Ali,
Md. Kamrul Hossain,
ABM Alauddin Chowdhury,
Alexandru Nedelea
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
113-123
Received:
3 July 2017
Accepted:
25 August 2017
Published:
30 November 2017
Abstract: The Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh has established Bangladesh NGO Foundation (BNF) to support the NGOs, with a view to associate the Non-Governmental Organizations and assigned to take up socio- economic development activities and poverty alleviation. The country has also been facing massive challenges of feeding the rapidly increasing population or even to support their livelihood in a sustainable manner. Bangladesh NGO foundation already disbursed more than 110 Crore taka through partner organizations out of which 36% is male while 64% is female beneficiary. The study intends to see whether SDG 1 and 5 is implementing through BNF or not. Time period of the study was 15 May 2016 to 30th June, 2017. This study aimed to find out whether sustainable development goal 1 and 5 of BNF partner organization due to BNF grant is indicating any significant role? Research question of the study is whether BNF’s partner organizations sustainable development goal 1 and 5 of BNF partner organization due to BNF grant? Self-administered questionnaires were used to collect the data for this study. NGOs are working for women’s entrepreneurship since expanding women’s economic opportunities is fundamental to sustainable growth and building more equitable societies. In this study, 93.9% of the organizations give help to women entrepreneurs. Majority (69.6%) of the respondents were strongly agreed that BNF’s financing and capital formatting solve social problem. It has been seen that there was significant association between NGOs role for removing poverty and fulfilling towards SDG1 and 5 as disparity of removing inequality of poor women group has been also occurring. Equitable justice and removing income inequality is occurring through BNF grant. However, restructuring of BNF is required as it lacks any vision, mission and marketing approach as well as supply chain management process. BNF also need to take a project to play as a financial intermediary to ensure community banking in Bangladesh under separate regulator.
Abstract: The Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh has established Bangladesh NGO Foundation (BNF) to support the NGOs, with a view to associate the Non-Governmental Organizations and assigned to take up socio- economic development activities and poverty alleviation. The country has also been facing massive challenges of feeding the rapidly incr...
Show More
-

Fitting Finite Mixtures of Generalized Linear Regressions on Motor Insurance Claims
Nana Kena Frempong,
Osei Tawiah Owusu,
Maxwell Akwasi Boateng,
Francis Kwame Bukari
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
124-128
Received:
1 March 2017
Accepted:
8 May 2017
Published:
7 December 2017
Abstract: The aim of this study is to determine the best mixture model for claim amount from a comprehensive insurance policy portfolio and use the model to estimate the expected claim amount per risk for the coming calendar year. The claims data were obtained from the motor insurance office of one of the top business insurance companies in Ghana. The data consists of one thousand (1,000) claim amounts from January 2012 to December 2014. The expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm within a maximum likelihood framework was used to estimate the parameters of four mixture models namely the Heterogeneous Normal-Normal, Homogeneous Normal-Normal, Pareto-Gamma and Gamma-Gamma. These mixture models were fitted to the claims data and measures of goodness-of-fit (AIC and BIC) were used to determine the best mixture model. The Heterogeneous Normal-Normal mixture distribution was the appropriate model for the motor insurance claims data due to the least AIC. The estimated expected claims amount for the coming calendar year (2015) from the model was GHS 877.672 per risk. This in a way may inform decision makers as to the kind of anticipated reserves for future claims.
Abstract: The aim of this study is to determine the best mixture model for claim amount from a comprehensive insurance policy portfolio and use the model to estimate the expected claim amount per risk for the coming calendar year. The claims data were obtained from the motor insurance office of one of the top business insurance companies in Ghana. The data c...
Show More
-

Stochastic Asset Models for Actuarial Use in Ghana
Evans Tee,
Eric Dei Ofosu-hene
Issue:
Volume 3, Issue 4, December 2017
Pages:
129-139
Received:
28 May 2017
Accepted:
12 June 2017
Published:
16 January 2018
Abstract: The need for stochastic asset models has evolved from a common global standard for risk management in the Solvency II regime in Europe, IAIS Common Principles, Global ORSA standards NAIC, EIOPA, and OSFI. But the challenges in developing markets such as; lack of good quality data, inconsistent data coverage, market data not having long enough history, and lack of liquidity in certain parts of asset market have caused the absence of such models in Ghana. There have been a number of actuarial stochastic asset models designed for simulating future economic and investment conditions in several parts of the world. This study has discussed three of such models and determined which best fits the Ghanaian economic data. The data used for the empirical analysis in this study were taken from the Bank of Ghana database and the Ghana Stock Exchange. The study re-calibrated the models to derive the parameter set then compared the model results numerically after running 10000 simulations for 50 horizons. Investigations about the basic statistics of the simulated results for all the models are compared. The analysis revealed that all of the Ghanaian investment series used in the stochastic investment modeling are non-stationary in their mean, variance and auto-covariance. The study then found that the “Wilkie linear model” produced simulated values with similar characteristics to the historical data whiles the Whitten & Thomas TAR model produced simulated values with minimal forecast error. The study therefore suggests that since the “Wilkie linear model” has a relatively better parsimony, ready economic interpretation and its ability to mimic some important features of the Ghanaian economic series it deserves the attention of the actuary seeking to model jointly the behavior of asset returns and economic variables that matter in economic capital determination of insurance and pension business in Ghana.
Abstract: The need for stochastic asset models has evolved from a common global standard for risk management in the Solvency II regime in Europe, IAIS Common Principles, Global ORSA standards NAIC, EIOPA, and OSFI. But the challenges in developing markets such as; lack of good quality data, inconsistent data coverage, market data not having long enough histo...
Show More









