In this study, cadmium Sulphide (CdS), a group II–VI semiconductor known for its wide applications in optoelectronics, piezoelectric devices, and other semiconductor technologies, and cobalt Sulphide (CoS), notable for its roles in solar-selective coatings, infrared sensing, and photo electrochemical energy storage, were investigated. Thin films of CdS, CoS, and their heterostructure (CdS/CoS and CoS/CdS) were synthesized via the chemical bath deposition (CBD) method at 80°C for 1.5 hours, using cadmium acetate, cobalt acetate, thioacetamide, and EDTA as precursor materials. The films were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and optical absorption spectroscopy. Optical measurements revealed that pure CdS and CoS films exhibited direct band gaps of 2.4 eV and 1.6 eV, respectively, at deposition pH values of 2.5 and 6. The heterostructure films showed dual band gaps of 2.4 eV (CdS) and 1.65 eV (CoS) for CdS/CoS, and 1.45 eV (CoS) and 2.5 eV (CdS) for CoS/CdS. SEM analyses indicated that CoS films were compact with uniformly distributed grains, while CdS films displayed smooth, spherical grains free of pinholes. The CdS/CoS layers appeared denser with occasional surface defects. XRD analysis confirmed that CdS and CoS/CdS films crystallized in a cubic structure with a preferred (111) orientation, CoS exhibited a hexagonal phase, and CdS/CoS composites displayed a mixed cubic–hexagonal structure. EDX results showed a near-stoichiometric Cd/S ratio (48:52) in CdS and validated the presence of Cd, Co, and S in all prepared samples.
| Published in | American Journal of Chemical Engineering (Volume 14, Issue 1) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12 |
| Page(s) | 8-18 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2026. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Heterostructure, Thin Films, Chemical Bath, Cobalt Sulphide, Cadmium Sulphide
Deposition Time | t (hr) | T (°C) | Cobalt Acetate | Cadmium Acetate | EDTA | Thioacetamide | PH | Vol. (l) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CoS | 1:30 | 80°C | 0.2M | 10ml | 0.2M | 22.5 ml | 0.2M | 9ml | 1M | 10ml | 6 | 51 |
CdS | 1:30 | 80°C | 0.2M | 22.5ml | 0.2M | 22.5 ml | 0.2M | 3ml | 1M | 10ml | 2.5 | 51 |
CdS/CoS | 1:30 | 80°C | 0.2M | 22.5ml | 0.2M | 3ml | 2.5M | 5ml | 1M | 10ml | 2.5 | 51 |
CoS/CdS | 1:30 | 80°C | 0.2M | 10ml | 0.2M | 22.5ml | 0.2M | 9ml | 1M | 10ml | 6 | 51 |
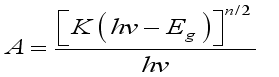
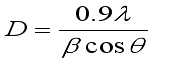
Sample | Standard values 2θ(deg) | hkl value | FWHM | 2θ(deg) | Observed intensity | Crystalline Size D(nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CoS | 19.465 | 1 1 1 | 0.11307 | 20.41675 | 1213.9504 | 71.4 |
22.478 | 2 0 0 | 0.11884 | 21,64609 | 326.78798 | 68 | |
32.228 | 2 2 0 | 0.12604 | 22.24599 | 584.83516 | 63 | |
37.858 | 3 1 1 | 8.94584 | 24.04519 | 108.35441 | 0.9 | |
39.509 | 2 2 2 | 230956.39872 | 30.7752 | 34.92437 | ||
45.825 | 4 0 0 | |||||
50.235 | 3 3 0 | |||||
45.825 | 4 0 0 | |||||
CdS | 26.547 | 1 11 | 2.2760 | 26.70272 | 69.46205 | 3.4 |
C0S/CdS | 1 1 1 | 0.26872 | 26.7937 | 2083.02523 | 30.3 | |
CdS/CoS | 2 0 0 | 0.42232 | 21.40356 | 103.81718 | 19 | |
230.93464 | 21.40356 | 26.9623 | 0.03 | |||
0.17769 | 26.53429 | 108.35278 | 74.6 | |||
0.27451 | 26.7085 | 147.84766 | 29.8 | |||
68.5608 | 26.785 | 39.95526 | 0.1 | |||
4 0 0 | 0.2004 | 45.74755 | 165.65453 | 43 |
CoS | Cobalt Sulfide |
CdS | Cadmium Sulfide |
CoS/CdS | Cobalt Sulfide over Cadmium Sulfide |
CdS/CoS | Cadmium Sulfide over Cobalt Sulfide |
CBD | Chemical Bath Deposition |
XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
UV-V | UV-Visible Spectroscopy |
EDX | Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| [1] | O. Calzadilla, F. Chale-lara, V. Rejonc, J.L. Pena, F. Caballero-Brionesa, "Mg-doped CdS films prepared by chemical bath deposition. optical," Chalcogenide Letters, April 2015 vol. 12, no. 4, p. 137 – 145. |
| [2] | K.mani, S. sagadevan, S.thirumavalavan, "Studies on Structural," Journal of Ovonic Research, 2015., vol. 11, no. 5, p. 203 – 211. |
| [3] | Hadi Ahmed Hussin, "Urbach energy and dispersion parameters of CdSchemically deposited thin films on the effect of thickness," international scientific journal 2018. pp. 241-249. |
| [4] | Ahmed N. Abd, "Improved Photoresponse of Porous Silicon Photodetectors by EmbeddingImproved Photoresponse of Porous Silicon Photodetectors by Embedding," 2016. J. Nano. Adv. Mat., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 33-44, 1. |
| [5] | R.Hepzi Pramila Devamani, "Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles," International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology,, January 2017, vol. 4, no. 1. |
| [6] | Robabe Mohammadzadeh-Hesar, Shahin Khademinia Leila Kafi-Ahmadi, "Influence of reactionparameters on crystal phase growth and optical properties of ultrasonic assisted Hydro-and solvothermal synthesized sub-micrometer-sized CdSspheres," Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2018., 9, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 346-356. |
| [7] | A. a. azizova, m. b. muradov, a. m. maharramov, g. m.eyvazova o. o. balayeva, "synthesis and characterization of cobalt sulfide/fnbrnanocomposites by silar method," journal of ovonic research november - 2016. vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 267 - 273, november - 2016. |
| [8] | Ofeliya O. Balayeva, Abdulsaid A. Azizova, Abel M. Maharramova, Lala R. Qahramanlib, Goncha M. Eyvazovab, Zohrab A. Aghamaliyevb Mustafa B. Muradovb, "Synthesis and characterization of cobalt sulfide nanoparticles by sonochemical method," ScienceDirect, june 2018. |
| [9] | M. S sonawane, R. spatill characterization of chemical deposited nano crystalline cobalt sulphide thin film. 3 2014. |
| [10] | Tizazu, A., et al., A New Route for the S. nthesis of CdS Thin Films from Acidic Chemical Baths. Int. J. Thin. Film Sci. Tec, 2017. 6(2): p. 67-71. |
| [11] | Mane, S., S. Kamble, and L. Deshmukh, Cobalt sulphide thin films: Chemical bath deposition, growth and properties. Materials Letters, 2011. 65(17-18): p. 2639-2641. |
| [12] | Markus Neuwirtha, Elisabeth Seydela, Jasmin Seeger, Alexander Welle Heinz Kalt, Michael Hetterich, B, "h, Band-gap tuning of Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 solar cell absorbers via definedincorporation of sulphur based on a post-sulphurization process," ScienceDirect 2018., pp. 158-165. |
| [13] | Francis Kofi Ampong, Fekadu Gashaw Hone, Robert Kwame Nkum, Francis Boaky Tizazu Abzaa, "Preparation of cadmium zinc sulfide (Cd1-xZnxS) thin films from acidic chemicalBAS,", ScienceDirect, 2018. no. 66, pp. 28-33. |
| [14] | K. Rajathi and A. Rajendran, "n Green Synthesis of Stable CdSNanoparticlesfrom Imidazolium Ionic Liquids and their Antibacterial Activities," Global Research Publications, January-March 2015.vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 1-8. |
| [15] | Andrzej Sikora, S.T. Pawar, N.N. Maldar, L.P. Deshmukh P A 5S.S. Kamble, "1 Cobalt sulfide thin films: Chemical growth, reaction kinetics and microstructuralanalyis,", ScienceDirect 2015., no. 623, p. 466-472. |
| [16] | Jose Luis G. Fierro and Rufino M. Navarro Yerga, Fernando Vaquero, "Nanowires of CdS Synthesized by a Solvothermal Method: Influence of the Morphologyon the Photoactivity for Hydrogen Evolution from Water," MDPI, March 2016 no. 24. |
| [17] | K. Manikandan, C. Surendra Dilip, P. Mani and J. Joseph Prince, 7, "Deposition and Characterization of CdS Nano Thin Film with Complexing Agent Triethanolamine," American journal oe Egnering and Applied science, 2015. |
| [18] | Rajeshwar Sharma, Raghvendra Singh Yadav, Diwakar Kashyap, S. L. Kothari S. Kachhwaha Aryan Sankhla, "a, Biosynthesis and characterization of cadmium sulfidenanoparticles e An emphasis of zeta potential behavior due to capping", ScienceDirect, 2015.pp. 1-8. |
| [19] | Gebremeskel Tekle, Eyobe Belew Abebe, and Kalid Seid Ahmed Tizazu Abza, "Characterization of Cobalt Sulfide Thin Films Synthesized from Acidic Chemical BAS," Hindawi. |
APA Style
Eshete, T. M., Somano, T. T. (2026). Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide (CdS) and Cobalt Sulphide (CoS) Heterostructure Using the Chemical Bath Deposition Method. American Journal of Chemical Engineering, 14(1), 8-18. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12
ACS Style
Eshete, T. M.; Somano, T. T. Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide (CdS) and Cobalt Sulphide (CoS) Heterostructure Using the Chemical Bath Deposition Method. Am. J. Chem. Eng. 2026, 14(1), 8-18. doi: 10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12
@article{10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12,
author = {Tangut Masreshaw Eshete and Takele Teshome Somano},
title = {Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide (CdS) and Cobalt Sulphide (CoS) Heterostructure Using the Chemical Bath Deposition Method},
journal = {American Journal of Chemical Engineering},
volume = {14},
number = {1},
pages = {8-18},
doi = {10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ajche.20261401.12},
abstract = {In this study, cadmium Sulphide (CdS), a group II–VI semiconductor known for its wide applications in optoelectronics, piezoelectric devices, and other semiconductor technologies, and cobalt Sulphide (CoS), notable for its roles in solar-selective coatings, infrared sensing, and photo electrochemical energy storage, were investigated. Thin films of CdS, CoS, and their heterostructure (CdS/CoS and CoS/CdS) were synthesized via the chemical bath deposition (CBD) method at 80°C for 1.5 hours, using cadmium acetate, cobalt acetate, thioacetamide, and EDTA as precursor materials. The films were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and optical absorption spectroscopy. Optical measurements revealed that pure CdS and CoS films exhibited direct band gaps of 2.4 eV and 1.6 eV, respectively, at deposition pH values of 2.5 and 6. The heterostructure films showed dual band gaps of 2.4 eV (CdS) and 1.65 eV (CoS) for CdS/CoS, and 1.45 eV (CoS) and 2.5 eV (CdS) for CoS/CdS. SEM analyses indicated that CoS films were compact with uniformly distributed grains, while CdS films displayed smooth, spherical grains free of pinholes. The CdS/CoS layers appeared denser with occasional surface defects. XRD analysis confirmed that CdS and CoS/CdS films crystallized in a cubic structure with a preferred (111) orientation, CoS exhibited a hexagonal phase, and CdS/CoS composites displayed a mixed cubic–hexagonal structure. EDX results showed a near-stoichiometric Cd/S ratio (48:52) in CdS and validated the presence of Cd, Co, and S in all prepared samples.},
year = {2026}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulphide (CdS) and Cobalt Sulphide (CoS) Heterostructure Using the Chemical Bath Deposition Method AU - Tangut Masreshaw Eshete AU - Takele Teshome Somano Y1 - 2026/02/06 PY - 2026 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12 DO - 10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12 T2 - American Journal of Chemical Engineering JF - American Journal of Chemical Engineering JO - American Journal of Chemical Engineering SP - 8 EP - 18 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2330-8613 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajche.20261401.12 AB - In this study, cadmium Sulphide (CdS), a group II–VI semiconductor known for its wide applications in optoelectronics, piezoelectric devices, and other semiconductor technologies, and cobalt Sulphide (CoS), notable for its roles in solar-selective coatings, infrared sensing, and photo electrochemical energy storage, were investigated. Thin films of CdS, CoS, and their heterostructure (CdS/CoS and CoS/CdS) were synthesized via the chemical bath deposition (CBD) method at 80°C for 1.5 hours, using cadmium acetate, cobalt acetate, thioacetamide, and EDTA as precursor materials. The films were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and optical absorption spectroscopy. Optical measurements revealed that pure CdS and CoS films exhibited direct band gaps of 2.4 eV and 1.6 eV, respectively, at deposition pH values of 2.5 and 6. The heterostructure films showed dual band gaps of 2.4 eV (CdS) and 1.65 eV (CoS) for CdS/CoS, and 1.45 eV (CoS) and 2.5 eV (CdS) for CoS/CdS. SEM analyses indicated that CoS films were compact with uniformly distributed grains, while CdS films displayed smooth, spherical grains free of pinholes. The CdS/CoS layers appeared denser with occasional surface defects. XRD analysis confirmed that CdS and CoS/CdS films crystallized in a cubic structure with a preferred (111) orientation, CoS exhibited a hexagonal phase, and CdS/CoS composites displayed a mixed cubic–hexagonal structure. EDX results showed a near-stoichiometric Cd/S ratio (48:52) in CdS and validated the presence of Cd, Co, and S in all prepared samples. VL - 14 IS - 1 ER -